What are the steps involved in the key generation process of the RSA cryptosystem, and why is the selection of large prime numbers crucial?
The RSA cryptosystem, named after its inventors Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman, is a cornerstone of public-key cryptography. The process of key generation in RSA involves several critical steps, each contributing to the security and functionality of the system. The selection of large prime numbers is fundamental to the strength of RSA encryption, as it directly impacts the difficulty of factorizing the public key, which is the basis of RSA's security.
The key generation process in RSA can be broken down into the following steps:
1. Selection of Two Large Prime Numbers
The first step in RSA key generation is to select two large prime numbers, denoted as Example:
Suppose ![]() and
and ![]() . These are relatively small primes for the sake of illustration, but in practice, much larger primes are used.
. These are relatively small primes for the sake of illustration, but in practice, much larger primes are used.
2. Compute 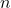 (the Modulus)
(the Modulus)
Once the primes ![]()
Example:
For ![]() and
and ![]() ,
,
![]()
3. Compute Euler's Totient Function 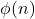
Euler's Totient Function, ![]()
This function counts the number of integers up to ![]() that are coprime with
that are coprime with ![]() .
.
Example:
For ![]() and
and ![]() ,
,
![]()
4. Choose the Public Exponent 
The public exponent Example:
Let ![]() . Check that
. Check that ![]() .
.
5. Compute the Private Exponent 
The private exponent ![]()
The Extended Euclidean Algorithm is typically used to find ![]() .
.
Example:
Using the Extended Euclidean Algorithm, we find ![]() such that:
such that:
![]()
The solution is ![]() .
.
6. Form the Public and Private Keys
The public key consists of the pair Example:
Public Key: ![]()
Private Key: ![]()
Importance of Large Prime Numbers
The security of the RSA cryptosystem relies heavily on the difficulty of factorizing the modulus 1. Factorization Difficulty: The primary reason large primes are important is the difficulty of the integer factorization problem. For sufficiently large ![]() , factorizing it into
, factorizing it into ![]() and
and ![]() is computationally intensive. The security of RSA is based on the assumption that integer factorization is a hard problem, meaning no efficient (polynomial time) algorithm exists for it.
is computationally intensive. The security of RSA is based on the assumption that integer factorization is a hard problem, meaning no efficient (polynomial time) algorithm exists for it.
2. Preventing Attacks: Small primes can be factored relatively quickly using modern algorithms like the General Number Field Sieve (GNFS). By using large primes, the time required to factor ![]() increases exponentially, making brute-force attacks impractical.
increases exponentially, making brute-force attacks impractical.
3. Ensuring Cryptographic Strength: The length of the keys (2048 bits or more) directly correlates with the cryptographic strength of RSA. Larger key sizes provide a higher level of security, which is necessary to protect against advances in computational power and algorithmic breakthroughs.
4. Prime Generation Algorithms: Efficient algorithms, such as the Miller-Rabin primality test, are used to generate and verify large primes. These algorithms ensure that the primes used in RSA key generation are indeed prime with a high degree of certainty.
Practical Example of RSA Encryption and Decryption
To illustrate the RSA process, consider the following example using the previously generated keys:
Encryption:
To encrypt a plaintext message ![]() (where
(where ![]() is an integer such that
is an integer such that ![]() ), the sender computes the ciphertext
), the sender computes the ciphertext ![]() using the recipient's public key
using the recipient's public key ![]() :
:
![]()
Example:
Let ![]() . Using the public key
. Using the public key ![]() ,
,
![]()
Decryption:
To decrypt the ciphertext ![]() , the recipient uses their private key
, the recipient uses their private key ![]() to compute the plaintext message
to compute the plaintext message ![]() :
:
![]()
Example:
Using the private key ![]() ,
,
![]()
This demonstrates that the original message ![]() is successfully recovered.The RSA key generation process involves the careful selection and computation of large prime numbers, which are fundamental to the security of the cryptosystem. The steps include selecting two large primes, computing their product and totient, choosing a public exponent, calculating the private exponent, and forming the public and private keys. The use of large primes ensures the difficulty of factorizing the modulus, thereby providing robust security against potential attacks.
is successfully recovered.The RSA key generation process involves the careful selection and computation of large prime numbers, which are fundamental to the security of the cryptosystem. The steps include selecting two large primes, computing their product and totient, choosing a public exponent, calculating the private exponent, and forming the public and private keys. The use of large primes ensures the difficulty of factorizing the modulus, thereby providing robust security against potential attacks.
Other recent questions and answers regarding EITC/IS/CCF Classical Cryptography Fundamentals:
- Is cryptography considered a part of cryptology and cryptanalysis?
- Will a shift cipher with a key equal to 4 replace the letter d with the letter h in ciphertext?
- Does the ECB mode breaks large input plaintext into subsequent blocks
- Do identical plaintext map to identical cipher text of a letter frequency analysis attact against a substitution cipher
- What is EEA ?
- Are brute force attack always an exhausive key search?
- In RSA cipher, does Alice need Bob’s public key to encrypt a message to Bob?
- Can we use a block cipher to build a hash function or MAC?
- What are initialization vectors?
- How many part does a public and private key has in RSA cipher
View more questions and answers in EITC/IS/CCF Classical Cryptography Fundamentals

