What is the parameter t of the extended eulers algoritm?
The parameter ![]() in the context of the Extended Euclidean Algorithm is a important component used primarily to find the multiplicative inverse of integers in modular arithmetic, which is a foundational concept in public-key cryptography. To understand the role and significance of
in the context of the Extended Euclidean Algorithm is a important component used primarily to find the multiplicative inverse of integers in modular arithmetic, which is a foundational concept in public-key cryptography. To understand the role and significance of ![]() , it is essential to consider the mechanics of the Extended Euclidean Algorithm and its applications in number theory and cryptography.
, it is essential to consider the mechanics of the Extended Euclidean Algorithm and its applications in number theory and cryptography.
The Euclidean Algorithm
The Euclidean Algorithm is a classical method for computing the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two integers. Given two integers ![]() and
and ![]() , where
, where ![]() , the Euclidean Algorithm repeatedly applies the division algorithm to express the GCD as:
, the Euclidean Algorithm repeatedly applies the division algorithm to express the GCD as:
![]()
This process continues until the remainder is zero. The last non-zero remainder is the GCD of ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
The Extended Euclidean Algorithm
The Extended Euclidean Algorithm extends the basic Euclidean Algorithm to not only find the GCD of two integers ![]() and
and ![]() but also to express this GCD as a linear combination of
but also to express this GCD as a linear combination of ![]() and
and ![]() . Specifically, it finds integers
. Specifically, it finds integers ![]() and
and ![]() such that:
such that:
![]()
These integers ![]() and
and ![]() are known as the Bézout coefficients. The algorithm proceeds by maintaining and updating these coefficients through each step of the Euclidean Algorithm.
are known as the Bézout coefficients. The algorithm proceeds by maintaining and updating these coefficients through each step of the Euclidean Algorithm.
Parameter 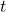 in the Extended Euclidean Algorithm
in the Extended Euclidean Algorithm
To illustrate the significance of ![]() , let's consider the steps of the Extended Euclidean Algorithm in more detail. Suppose we are given two integers
, let's consider the steps of the Extended Euclidean Algorithm in more detail. Suppose we are given two integers ![]() and
and ![]() with
with ![]() .
.
1. Initialization: Start with ![]() and
and ![]() . Initialize the coefficients:
. Initialize the coefficients:
![]()
2. Iteration: For each step ![]() , compute the quotient and remainder:
, compute the quotient and remainder:
![]()
Update ![]() and
and ![]() :
:
![]()
Update the coefficients:
![]()
3. Termination: The algorithm terminates when ![]() . At this point,
. At this point, ![]() is the GCD of the original
is the GCD of the original ![]() and
and ![]() , and
, and ![]() and
and ![]() are the Bézout coefficients.
are the Bézout coefficients.
Example
Consider finding the GCD of 240 and 46, and expressing it as a linear combination.
1. Initialization:
![]()
![]()
2. First Iteration:
![]()
![]()
![]()
3. Second Iteration:
![]()
![]()
![]()
4. Third Iteration:
![]()
![]()
![]()
5. Fourth Iteration:
![]()
![]()
![]()
6. Fifth Iteration:
![]()
![]()
![]()
The algorithm terminates at this point, with ![]() being the GCD of 240 and 46. The Bézout coefficients are
being the GCD of 240 and 46. The Bézout coefficients are ![]() and
and ![]() , giving us the equation:
, giving us the equation:
![]()
Application in Cryptography
In the realm of public-key cryptography, particularly within the RSA algorithm, the Extended Euclidean Algorithm is employed to find the modular inverse. Given an integer ![]() (the public exponent) and
(the public exponent) and ![]() (Euler's totient function of
(Euler's totient function of ![]() ), the goal is to find an integer
), the goal is to find an integer ![]() (the private exponent) such that:
(the private exponent) such that:
![]()
This is equivalent to finding ![]() such that:
such that:
![]()
for some integer ![]() . Here,
. Here, ![]() is the multiplicative inverse of
is the multiplicative inverse of ![]() modulo
modulo ![]() . The Extended Euclidean Algorithm is used to compute this
. The Extended Euclidean Algorithm is used to compute this ![]() .
.
The parameter ![]() in the Extended Euclidean Algorithm is essentially the quotient
in the Extended Euclidean Algorithm is essentially the quotient ![]() at each step of the algorithm. These quotients are used to iteratively update the coefficients
at each step of the algorithm. These quotients are used to iteratively update the coefficients ![]() and
and ![]() until the GCD is found. The Extended Euclidean Algorithm's ability to find these coefficients is what makes it invaluable in cryptographic applications, particularly in finding modular inverses which are important for key generation and encryption/decryption processes in public-key cryptography.
until the GCD is found. The Extended Euclidean Algorithm's ability to find these coefficients is what makes it invaluable in cryptographic applications, particularly in finding modular inverses which are important for key generation and encryption/decryption processes in public-key cryptography.
Other recent questions and answers regarding EITC/IS/CCF Classical Cryptography Fundamentals:
- Is cryptography considered a part of cryptology and cryptanalysis?
- Will a shift cipher with a key equal to 4 replace the letter d with the letter h in ciphertext?
- Does the ECB mode breaks large input plaintext into subsequent blocks
- Do identical plaintext map to identical cipher text of a letter frequency analysis attact against a substitution cipher
- What is EEA ?
- Are brute force attack always an exhausive key search?
- In RSA cipher, does Alice need Bob’s public key to encrypt a message to Bob?
- Can we use a block cipher to build a hash function or MAC?
- What are initialization vectors?
- How many part does a public and private key has in RSA cipher
View more questions and answers in EITC/IS/CCF Classical Cryptography Fundamentals

